performance.md 7.2 KB
Timescaledb - Performance
Pages: 2
Alerting
URL: llms-txt#alerting
Contents:
- Grafana
- Other alerting tools
Early issue detecting and prevention, ensuring high availability, and performance optimization are only a few of the reasons why alerting plays a major role for modern applications, databases, and services.
There are a variety of different alerting solutions you can use in conjunction with Tiger Cloud that are part of the Postgres ecosystem. Regardless of whether you are creating custom alerts embedded in your applications, or using third-party alerting tools to monitor event data across your organization, there are a wide selection of tools available.
Grafana is a great way to visualize your analytical queries, and it has a first-class integration with Tiger Data products. Beyond data visualization, Grafana also provides alerting functionality to keep you notified of anomalies.
Within Grafana, you can [define alert rules][define alert rules] which are time-based thresholds for your dashboard data (for example, "Average CPU usage greater than 80 percent for 5 minutes"). When those alert rules are triggered, Grafana sends a message via the chosen notification channel. Grafana provides integration with webhooks, email and more than a dozen external services including Slack and PagerDuty.
To get started, first download and install [Grafana][Grafana-install]. Next, add a new [Postgres data source][PostgreSQL datasource] that points to your Tiger Cloud service. This data source was built by Tiger Data engineers, and it is designed to take advantage of the database's time-series capabilities. From there, proceed to your dashboard and set up alert rules as described above.
Alerting is only available in Grafana v4.0 and later.
Other alerting tools
Tiger Cloud works with a variety of alerting tools within the Postgres ecosystem. Users can use these tools to set up notifications about meaningful events that signify notable changes to the system.
Some popular alerting tools that work with Tiger Cloud include:
- [DataDog][datadog-install]
- [Nagios][nagios-install]
- [Zabbix][zabbix-install]
See the [integration guides][integration-docs] for details.
===== PAGE: https://docs.tigerdata.com/use-timescale/data-retention/ =====
Improve query and upsert performance
URL: llms-txt#improve-query-and-upsert-performance
Contents:
- Segmenting and ordering data
- Improve performance in the columnstore by segmenting and ordering data
Real-time analytics applications require more than fast inserts and analytical queries. They also need high performance when retrieving individual records, enforcing constraints, or performing upserts, something that OLAP/columnar databases lack. This pages explains how to improve performance by segmenting and ordering data.
To improve query performance using indexes, see [About indexes][about-index] and [Indexing data][create-index].
Segmenting and ordering data
To optimize query performance, TimescaleDB enables you to explicitly control the way your data is physically organized in the columnstore. By structuring data effectively, queries can minimize disk reads and execute more efficiently, using vectorized execution for parallel batch processing where possible.
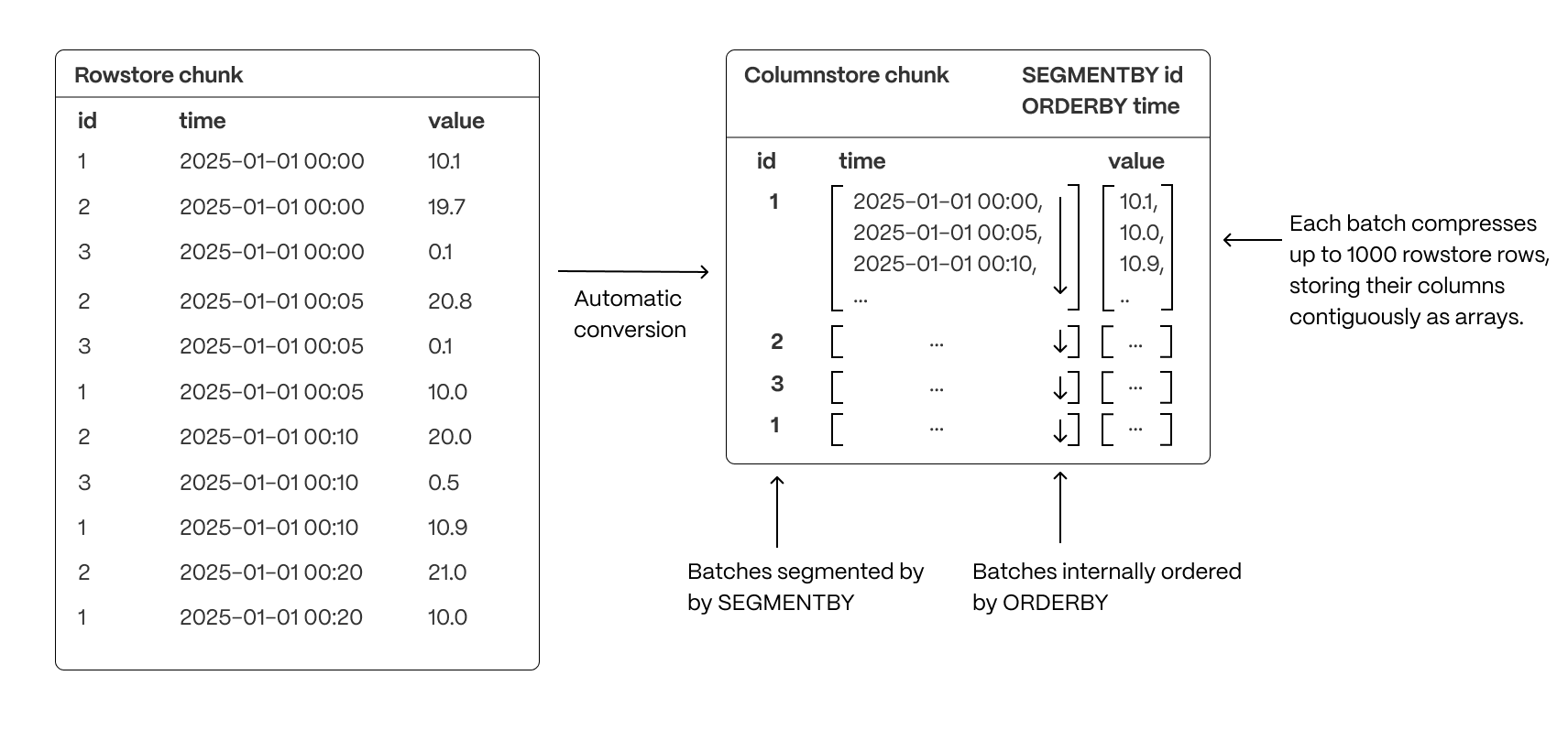
- Group related data together to improve scan efficiency: organizing rows into logical segments ensures that queries filtering by a specific value only scan relevant data sections. For example, in the above, querying for a specific ID is particularly fast.
- Sort data within segments to accelerate range queries: defining a consistent order reduces the need for post-query sorting, making time-based queries and range scans more efficient.
- Reduce disk reads and maximize vectorized execution: a well-structured storage layout enables efficient batch processing (Single Instruction, Multiple Data, or SIMD vectorization) and parallel execution, optimizing query performance.
By combining segmentation and ordering, TimescaleDB ensures that columnar queries are not only fast but also resource-efficient, enabling high-performance real-time analytics.
Improve performance in the columnstore by segmenting and ordering data
Ordering data in the columnstore has a large impact on the compression ratio and performance of your queries. Rows that change over a dimension should be close to each other. As hypertables contain time-series data, they are partitioned by time. This makes the time column a perfect candidate for ordering your data since the measurements evolve as time goes on.
If you use orderby as your only columnstore setting, you get a good enough compression ratio to save a lot of
storage and your queries are faster. However, if you only use orderby, you always have to access your data using the
time dimension, then filter the rows returned on other criteria.
Accessing the data effectively depends on your use case and your queries. You segment data in the columnstore to match the way you want to access it. That is, in a way that makes it easier for your queries to fetch the right data at the right time. When you segment your data to access specific columns, your queries are optimized and yield even better performance.
For example, to access information about a single device with a specific device_id, you segment on the device_id column.
This enables you to run analytical queries on compressed data in the columnstore much faster.
For example for the following hypertable:
Execute a query on a regular hypertable
- Query your data
Gives the following result:
- Query your data
Execute a query on the same data segmented and ordered in the columnstore
Control the way your data is ordered in the columnstore:
Query your data
Gives the following result:
As you see, using orderby and segmentby not only reduces the amount of space taken by your data, but also
vastly improves query speed.
The number of rows that are compressed together in a single batch (like the ones we see above) is 1000. If your chunk does not contain enough data to create big enough batches, your compression ratio will be reduced. This needs to be taken into account when you define your columnstore settings.
===== PAGE: https://docs.tigerdata.com/use-timescale/hypercore/modify-data-in-hypercore/ =====
Examples:
Example 1 (sql):
CREATE TABLE metrics (
time TIMESTAMPTZ,
user_id INT,
device_id INT,
data JSONB
) WITH (
tsdb.hypertable,
tsdb.partition_column='time'
);
Example 2 (sql):
SELECT device_id, AVG(cpu) AS avg_cpu, AVG(disk_io) AS avg_disk_io
FROM metrics
WHERE device_id = 5
GROUP BY device_id;
Example 3 (sql):
device_id | avg_cpu | avg_disk_io
-----------+--------------------+---------------------
5 | 0.4972598866221261 | 0.49820356730280524
(1 row)
Time: 177,399 ms
Example 4 (sql):
ALTER TABLE metrics SET (
timescaledb.enable_columnstore = true,
timescaledb.orderby = 'time',
timescaledb.segmentby = 'device_id'
);